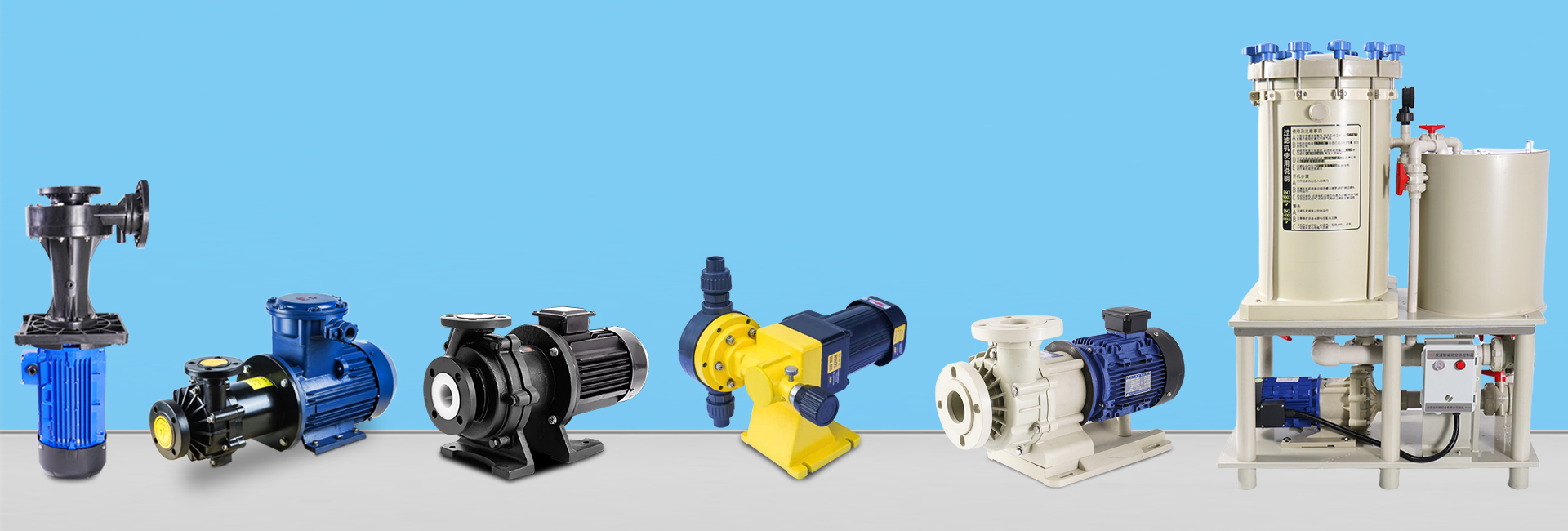
In today’s world of increasingly stringent environmental regulations and complex industrial processes, water treatment systems — such as wastewater treatment, chemical processing, or electroplating — often require the transfer of highly corrosive fluids. Faced with numerous pump options, one critical question arises:

How do you choose the right pump for corrosive media in your water treatment project?
The answer lies in matching the chemical properties of the fluid with the correct pump type and material. Below are five common types of corrosion-resistant pumps, each designed for specific working conditions and fluid characteristics.
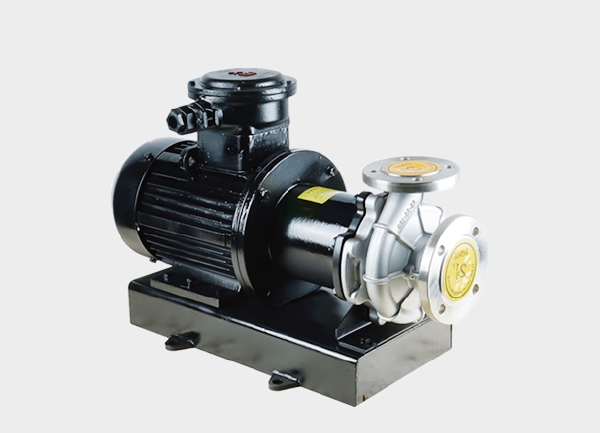
1. Corrosion-Resistant Pump
This is a broad category that includes all pumps with wetted parts made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, PP (polypropylene), PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride), or PTFE (Teflon).
When your application involves general corrosive fluids and you’re at an early stage of pump selection, this term — “corrosion-resistant pump” — is a good starting point.
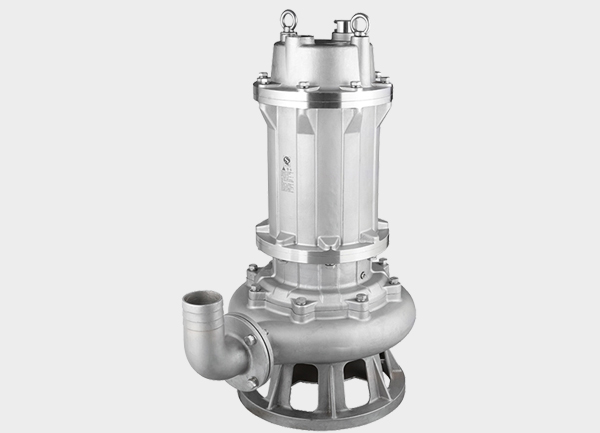
2. Corrosion-Resistant Submersible Pump
The keyword here is “submersible.”
This type of pump is designed to operate fully submerged in liquid and is commonly used for tank drainage, pit dewatering, or emergency pumping.
If your corrosive liquid is stored in a deep pit or tank bottom, a corrosion-resistant submersible pump is the ideal solution.
3. Corrosion-Resistant Sewage Pump
The focus here is on “sewage.”
These pumps are not only resistant to chemical corrosion but are also built to handle solid particles and fibrous impurities.
They are indispensable in processes involving chemical wastewater, dyeing wastewater, or pharmaceutical effluents, where the medium is both corrosive and contains suspended solids.
4. Corrosion-Resistant Wastewater Pump
Similar to sewage pumps, this type is designed for complex industrial wastewater that may contain a mix of acids, alkalis, and salts.
It emphasizes comprehensive chemical compatibility and durability, making it a core component in industrial wastewater treatment systems where multiple corrosive agents are present.
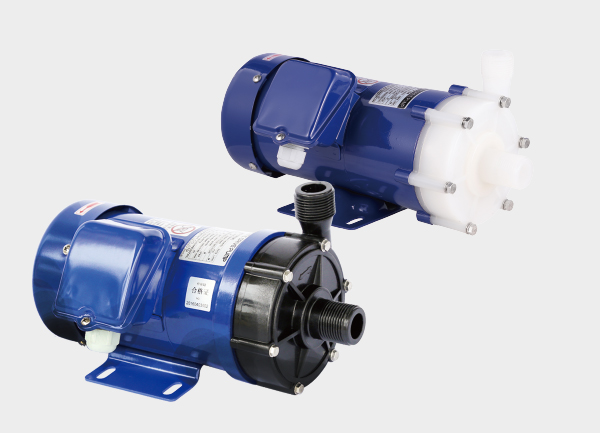
5. Chemical Pump for Corrosive Liquids
This is a specialized pump for transferring high-purity or hazardous chemicals such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, or hydrofluoric acid.
These pumps demand exceptional sealing integrity (often using magnetic drive mechanisms to ensure zero leakage), chemical resistance (PTFE or other fluoroplastics), and safety.
They are widely used in laboratories, chemical dosing systems, and precision chemical production lines.