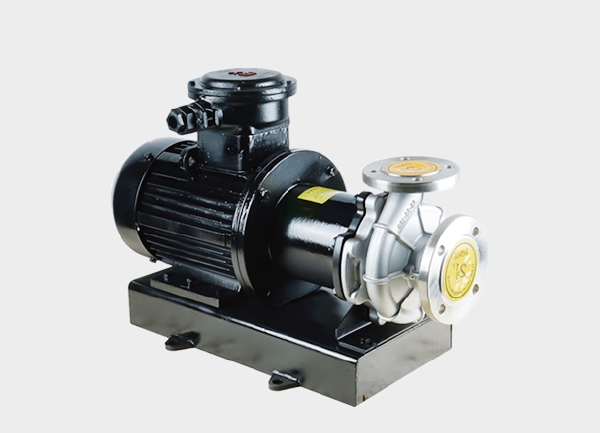
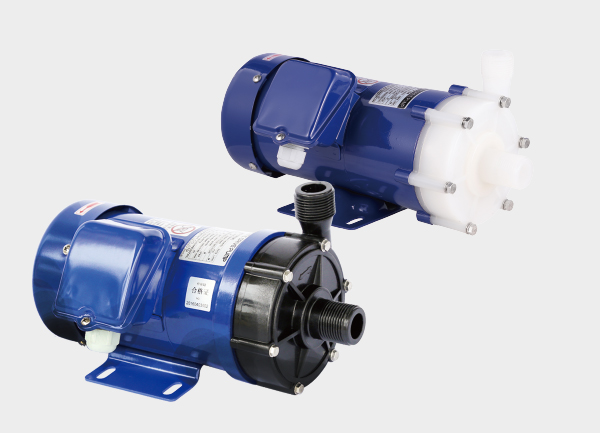
Both pump types belong to the “leak-free” magnetic drive category, but their core difference lies in the wetted material—the part that contacts the fluid. This single factor determines their corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and ideal applications. In short, stainless steel magnetic drive pumps emphasize strength and versatility, while fluoroplastic magnetic drive pumps excel in handling highly corrosive chemicals.

I. Core Differences
| Comparison Aspect | Stainless Steel Magnetic Drive Pump | Fluoroplastic Magnetic Drive Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Main Material | 304, 316L stainless steel | F46 (PFA), PVDF, or other fluoroplastics |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resistant to neutral or mild acids/alkalis; not suitable for strong corrosives (e.g., concentrated HCl, aqua regia) | Excellent resistance to almost all strong acids, bases, and solvents — the “King of Corrosion Resistance” |
| Applicable Media | Water, oil, weak acids/alkalis, low-concentration chemical solutions | Concentrated HCl, H₂SO₄, HNO₃, strong alkalis, and organic solvents |
| Temperature Range | Wide: -20℃ to 120℃ (some models up to 200℃) | Narrower: typically -20℃ to 80℃ (high heat may deform plastic) |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact and pressure resistance, long service life | Lower strength; vulnerable to impact and long-term aging |
| Cost | Moderate (lower raw material cost) | Higher (expensive raw materials and processing) |
II. Key Advantages of Each Pump
1. Advantages of Stainless Steel Magnetic Drive Pumps
Wide application range – Suitable for water, oils, beverages, and weakly corrosive solutions, widely used in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
High temperature and pressure tolerance – Performs reliably under high temperatures (above 80℃) or pressures without deformation or performance loss.
Excellent cost-performance ratio – Lower material cost and higher mechanical durability result in longer service life and lower maintenance expenses.
2. Advantages of Fluoroplastic Magnetic Drive Pumps
Superior corrosion resistance – The ideal solution for highly corrosive media such as concentrated acids, alkalis, and solvents that stainless steel cannot handle.
Anti-adhesion properties – Smooth inner surfaces reduce buildup and clogging, making it ideal for viscous or impurity-containing fluids.
Outstanding chemical stability – Fluoroplastics do not react with most chemicals, ensuring safe operation and maintaining fluid purity.
III. Key Selection Guidelines
1. Focus on corrosion level:
For highly corrosive fluids (e.g., ≥30% hydrochloric acid or organic solvents), choose fluoroplastic magnetic drive pumps.
For water, oils, or weakly corrosive fluids, stainless steel magnetic drive pumps are more economical.
2. Consider temperature and pressure:
For media above 80℃ or pressures ≥1.6 MPa, stainless steel is the better option.
For low-temperature, low-pressure but highly corrosive conditions, fluoroplastic pumps are ideal.
3. Evaluate cost and maintenance:
For long-term use with non-corrosive media, stainless steel offers the best cost efficiency.
For strong corrosive environments, fluoroplastic pumps prevent costly downtime or equipment damage.
Conclusion
Choosing between a stainless steel magnetic drive pump and a fluoroplastic magnetic drive pump ultimately depends on the corrosiveness, temperature, and pressure of the medium being handled. Stainless steel models deliver strength, reliability, and economy, while fluoroplastic pumps ensure absolute chemical resistance and safety. Selecting the right type ensures stable operation, extended service life, and optimal cost-effectiveness in industrial applications.