1. Overview
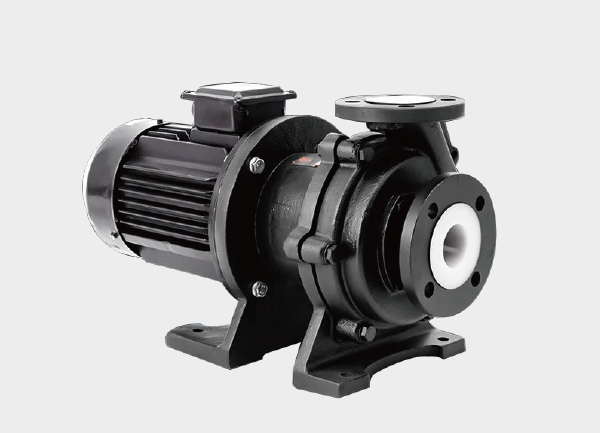
The PTFE-lined magnetic drive pump is a leak-free, corrosion-resistant, and highly reliable type of pump. It is a specialized form of a magnetically driven centrifugal pump (MDCP). The key feature of this pump is its internal lining made of fluoropolymer materials such as PTFE, FEP, or PFA, which effectively resist strong acids, strong alkalis, and various corrosive chemical media.
This type of pump is widely used in chemical, pharmaceutical, electronics, environmental protection, and petroleum industries, making it ideal for handling highly corrosive and high-purity liquids.
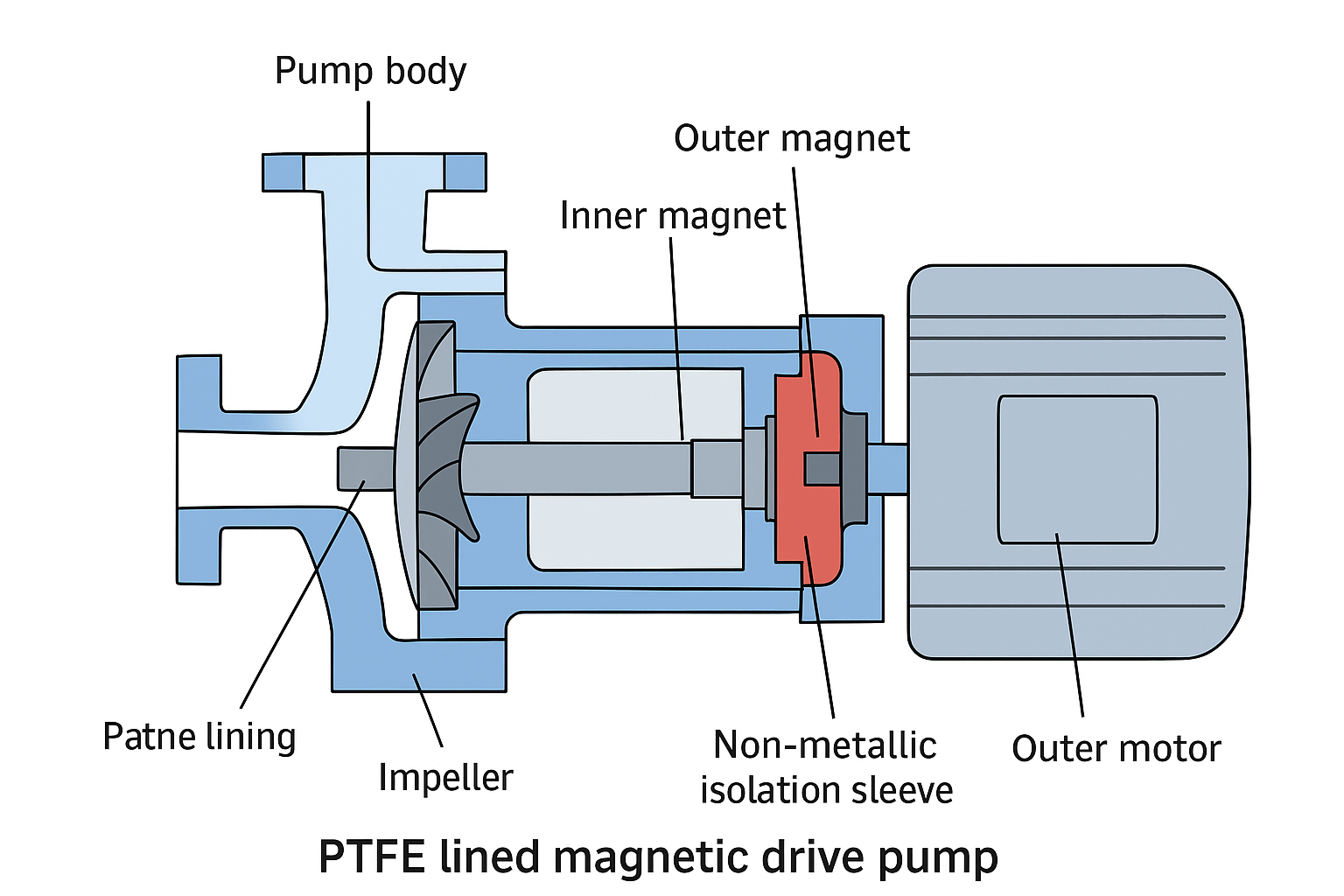
2. Structural Features
The PTFE-lined magnetic drive pump mainly consists of the following components:
Pump Casing and Lining
The pump casing and cover are typically made of metals such as cast iron or stainless steel, internally lined with fluoropolymer material.
The PTFE lining provides excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low friction, thereby extending the pump’s service life.
Magnetic Drive Assembly
Inner magnetic rotor: Directly connected to the pump shaft, driving the impeller.
Outer magnetic rotor: Connected to the motor or drive unit, transmitting torque through magnetic coupling.
Non-metallic isolation sleeve (PTFE or similar): Separates the inner and outer magnets, ensuring the fluid is completely isolated from the external environment.
Impeller
Typically made of fluoropolymer or corrosion-resistant metal.
Designed as a closed or semi-open impeller to optimize fluid dynamics efficiency.
Static Seals
Magnetic drive pumps do not require mechanical seals between the pump chamber and shaft, achieving near-zero leakage.
3. Working Principle
The PTFE-lined magnetic drive pump operates based on non-contact magnetic coupling, as follows:
The motor drives the outer magnetic rotor to rotate.
The magnetic field of the outer rotor transmits torque through the isolation sleeve to the inner magnetic rotor.
The inner rotor drives the impeller, which draws in liquid and generates centrifugal force, pushing the fluid toward the pump outlet.
The PTFE lining prevents corrosive liquids from contacting the metal casing, ensuring long-term, leak-free operation.
Key Advantage: Magnetic coupling eliminates the need for a shaft to penetrate the pump casing, providing complete isolation between the pump body and drive unit. This is the core technology that enables the PTFE-lined magnetic drive pump to be completely leak-free.
4. Advantages
Strong Corrosion Resistance
Fluoropolymer materials withstand acids, alkalis, oxidizing agents, and most organic solvents with excellent durability.
Leak-Free Operation
Eliminates the risk of mechanical seal leakage, making it ideal for toxic, high-purity, or flammable liquids.
Low Maintenance
No mechanical seals reduce maintenance frequency and extend pump lifespan.
Reliable Sealing
Non-contact magnetic coupling reduces pump wear, enhancing safety and reliability.
Suitable for Harsh Conditions
Capable of operating long-term under high temperature, high corrosion, strong acid, or strong alkali environments.
5. Applications
PTFE-lined magnetic drive pumps are widely used in:
Chemical Industry: Handling highly corrosive liquids such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid, or caustic soda.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Transporting high-purity solutions without contamination.
Electronics Industry: Circulating high-purity water or corrosive chemical reagents.
Environmental Protection: Treating acidic or alkaline wastewater.
6. Selection Guidelines
When selecting a PTFE-lined magnetic drive pump, consider:
Fluid Characteristics: Corrosiveness, viscosity, temperature, and solid content.
Flow Rate and Head: Determine pump size and power according to process requirements.
Material Selection: Choose the appropriate fluoropolymer lining (PTFE, FEP, etc.) based on the fluid’s corrosiveness.
Temperature Compatibility: Standard PTFE can handle 120–150°C, while special high-temperature applications require specialized materials.
7. Conclusion
The PTFE-lined magnetic drive pump offers corrosion resistance, leak-free operation, long service life, and low maintenance, making it a critical component in industries with demanding requirements such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and electronics.
Its core technologies—magnetic coupling transmission and PTFE lining—enable it to perform reliably in conditions where conventional pumps cannot. Understanding its working principle aids in proper selection, maintenance, and insight into modern industrial pump technology.








