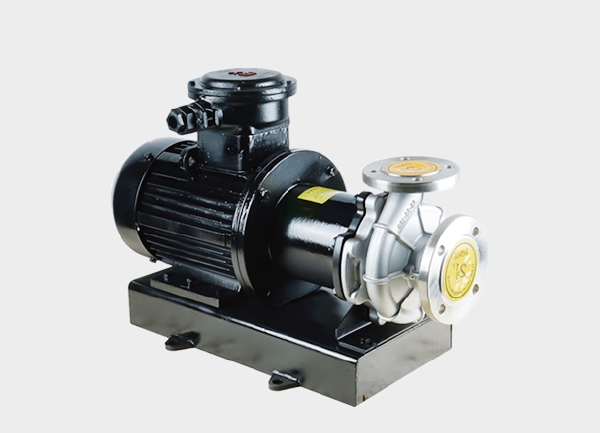
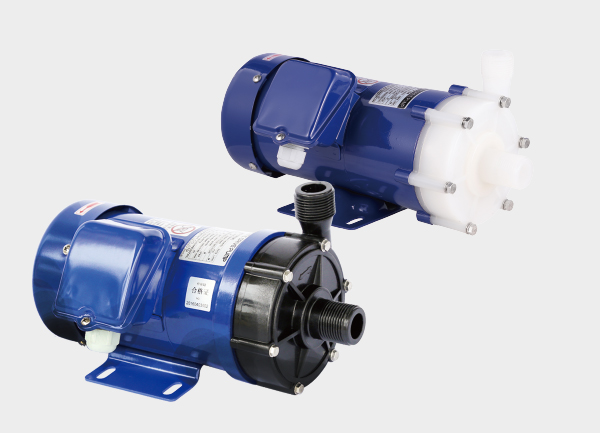
In the modern industrial sector, the importance of liquid transfer equipment is undeniable. Among various pump types, magnetic drive pumps have become the preferred choice for many industries thanks to their leak-free design, durability, and outstanding performance.
But what exactly is a magnetic drive pump, and why is it so widely used? Let’s explore the working principle, advantages, and main application fields of magnetic drive pumps.

1. Working Principle of Magnetic Drive Pumps
The core technology of a magnetic drive pump is based on magnetic coupling. The pump consists of several key components:
Motor
Outer magnetic rotor
Inner magnetic rotor
Isolation sleeve (non-magnetic material)
Impeller
Here’s how it works:
When the motor runs, it drives the outer magnetic rotor to rotate.
The rotating magnetic field passes through the isolation sleeve and drives the inner magnetic rotor.
The inner magnetic rotor is connected to the pump shaft and impeller, causing the impeller to rotate.
As the impeller rotates, liquid is sucked in through the pump inlet and discharged through the outlet under centrifugal force.
This non-contact power transmission eliminates the need for traditional mechanical shaft seals. As a result, it completely avoids leakage issues caused by wear or aging seals—making magnetic pumps a safer and more reliable liquid transfer solution.
2. Key Advantages of Magnetic Drive Pumps
✔ Leak-Free Operation
Unlike traditional pumps that rely on shaft seals, magnetic drive pumps use magnetic coupling. The shaft and inner magnetic rotor are fully enclosed, preventing leakage of toxic, flammable, explosive, or corrosive liquids. This ensures environmental and workplace safety.
✔ Longer Service Life
With no mechanical contact between moving parts, wear is significantly reduced. This means fewer failures, lower maintenance costs, and a longer service life.
✔ Stable and Quiet Operation
Non-contact transmission reduces vibration and noise, creating a more comfortable work environment and reducing risks of equipment damage.
✔ Wide Material Options
Flow-through components can be made from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, reinforced polypropylene, PTFE, graphite, and ceramics. This makes magnetic pumps adaptable for handling different corrosive or high-purity liquids.
3. Applications of Magnetic Drive Pumps
Thanks to their safety, durability, and corrosion resistance, magnetic drive pumps are used across multiple industries:
Chemical Industry
Ideal for transferring corrosive chemicals like strong acids, alkalis, and solvents. Commonly used in raw material transfer, reaction processes, and product handling.Pharmaceutical Industry
Ensures hygiene and purity by preventing leakage and contamination during the transfer of pharmaceutical raw materials and liquid medicines.Petroleum Industry
Provides safe, leak-free transfer of flammable and explosive products such as oil and refined fuels, reducing risks of accidents.Environmental Protection
Used in wastewater treatment and pollution control, magnetic drive pumps handle liquids containing pollutants without secondary leakage.Food and Beverage Industry
Flow-through parts can be manufactured with food-grade materials, ensuring hygienic transfer of beverages, flavorings, and other liquid food products.
Conclusion
With their innovative design, leak-free performance, and versatile applications, magnetic drive pumps have become an essential part of modern industry. They are widely used in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, petroleum, environmental protection, and food production.
As technology advances, magnetic drive pumps will continue to improve in efficiency, safety, and material adaptability, providing even more reliable solutions for industrial liquid transfer.