In chemical, environmental, and pharmaceutical industries, specialized vertical pumps have evolved to meet specific requirements such as submerged installation, highly corrosive media, and deep tank or sump pumping. This article explores six key types of vertical pumps—Extended Submersible Sewage Pumps, Long-Shaft Vertical Submersible Pumps, Stainless Steel Vertical Submersible Pumps, Vertical Chemical Pumps, PVDF External Sump Pumps, and Submersible Chemical Pumps—detailing their design, material advantages, and suitable industrial applications, providing precise guidance for pump selection.
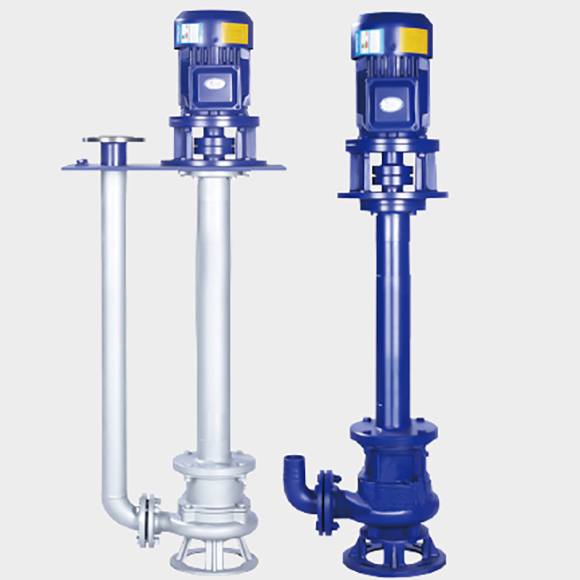

Vertical Pumps
1. Submersible Sewage Vertical Pumps: Handling Deep Sump Wastewater
1.1 Extended Submersible Sewage Pumps (Deep Sump & Debris Handling)
Structural Highlights:
Features an extended submerged shaft and segmented pump body, with immersion depths customizable from 1–5 m (up to 10 m max). Eliminates the need for a conventional pump pit.
Open double-blade impeller with bottom stirring teeth breaks down fibers and plastic debris to prevent clogging.
Dual mechanical seals with oil chamber lubrication protect the motor from wastewater intrusion, ensuring long-term submerged operation.
Material & Medium Compatibility:
Pump casing/impeller materials: Cast iron (standard wastewater), 304 stainless steel (lightly corrosive), 316L stainless steel (salt-containing or weak acid/alkaline wastewater).
Can handle solids ≤50 mm, fibrous debris, temperatures ≤80°C, viscosity ≤800 cSt.
Typical Applications:
Chemical wastewater: Sump discharge in chemical plants, e.g., pesticide production containing residue.
Environmental engineering: Large sedimentation tank sludge, landfill leachate extraction.
Metallurgy: Cooling water tanks in steel mills with iron oxide debris, electroplating wastewater with small metallic solids.
1.2 Long-Shaft Vertical Submersible Pumps (Long-Distance Submerged Transfer)
Design Advantages:
Uses rigid long shaft with intermediate bearings, allowing shafts to extend up to 20 m.
Motor remains on the platform while the submerged pump operates via the long shaft.
Single/multi-stage centrifugal pump design delivers higher flow (up to 500 m³/h) and head (up to 150 m) for deep or high-head pumping.
Key Features:
Equipped with shaft vibration monitoring to prevent eccentric wear.
Submerged section has non-clogging flow paths, handling small solids ≤10 mm; not suitable for fibrous media.
Typical Applications:
Petrochemical: Deep crude oil tank extraction, viscous tar transfer in coking plants.
Power generation: Submerged circulation in thermal power plant water pools, gypsum slurry circulation in desulfurization towers.
Municipal: Deep rainwater pump stations (up to 20 m), clean water tanks in water treatment plants.
2. Submersible Chemical Pumps: Corrosion Resistance + Submerged Installation
2.1 Stainless Steel Vertical Submersible Pumps (Medium Corrosion)
Material & Corrosion Protection:
Pump body, impeller, and shaft sleeve: 304/316L stainless steel (316L superior for chloride resistance).
Sealing faces: silicon carbide + graphite, resistant to weak acid/alkaline media.
Submerged section has no exposed bolts, welded or flanged sealing to prevent leaks.
Structural Adaptation:
Single-stage: low head (≤50 m), high flow;
Multi-stage: high head (≤120 m), low flow.
Immersion depth: 1–8 m; motor protection: IP54/IP55.
Typical Applications:
Pharmaceutical: Bottom extraction of herbal extract or fermentation liquid with minimal mycelium.
Food processing: Tomato paste (acidic) or syrup (high concentration) transfer; prevents air exposure and spoilage.
Electroplating: Nickel/chrome plating tanks (sulfuric or hydrochloric acid) liquid circulation.
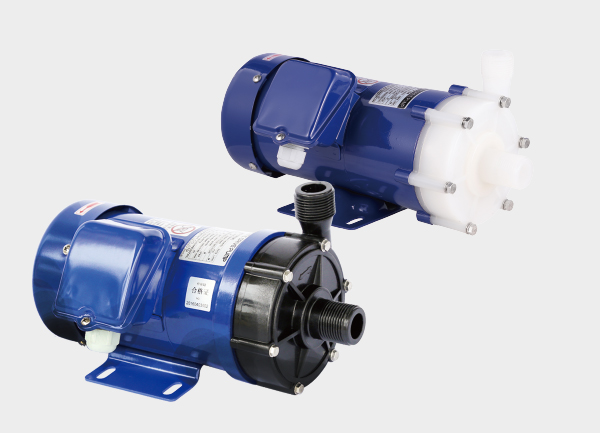
2.2 Submersible Chemical Pumps (High Corrosion & Toxic Media)
Corrosion & Safety Upgrades:
Pump body: PTFE/FEP fluoroplastics or Hastelloy C276, resistant to strong acids (e.g., 98% sulfuric acid, 30% hydrochloric acid).
Magnetic drive (seal-less) ensures zero leakage for toxic, flammable, or explosive media.
Structural Details:
Submerged section: shaftless design, motor isolated via magnetic coupling.
Features temperature monitoring and magnetic overload protection to prevent overheating or blockage damage.
Typical Applications:
Fine chemicals: Toxic azo dye wastewater, organophosphate intermediates.
Hazardous waste treatment: Heavy-metal (Hg, Cd) acidic waste extraction.
Chemical fibers: High-temperature (200°C) polyester tank bottoms, corrosive glycol solutions.
3. External Sump & General Chemical Vertical Pumps
3.1 PVDF External Sump Pumps (High Corrosion & External Installation)
Material Benefits:
PVDF pump body, impeller, and casing: lightweight, high corrosion resistance, withstands -40~150°C, strong acids, bases, and organic solvents.
External Installation Advantages:
Pump sits outside the tank, suction pipe reaches inside; ideal for shallow tanks ≤2 m or where submersion is prohibited.
Flanged inlets/outlets integrate with chemical piping for pressurization or long-distance transfer.
Typical Applications:
Semiconductor: Wafer cleaning tanks (HF, ammonia) for corrosion-free circulation.
Coatings: Solvent-based coatings (toluene, xylene) transfer without metal corrosion.
Lab/Research: Small chemical experiments, strong acids like trifluoroacetic acid.
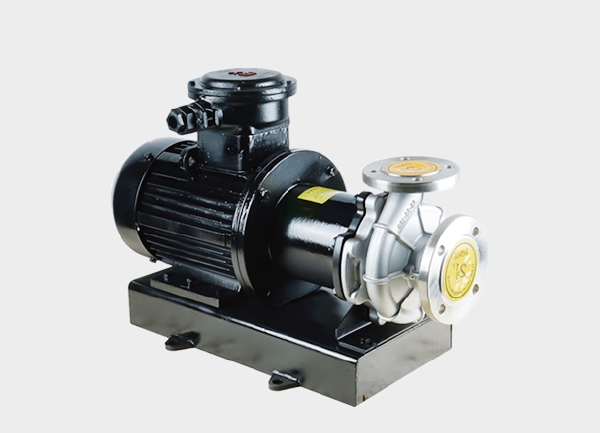
3.2 General Vertical Chemical Pumps (Pipeline Transport)
Structure & Use:
Non-submerged vertical centrifugal pump for chemical pipelines.
Horizontal inlet/outlet, mounted on pipeline supports; footprint ¼ of a horizontal pump.
Single-stage or multi-stage; head 10–200 m, flow 5–1000 m³/h.
Material & Sealing Options:
Base: 304 stainless steel; upgrade: 316L or fluoroplastic lining for strong corrosion.
Seal options: single mechanical seal (standard), double mechanical + nitrogen seal (toxic/explosive media).
Typical Applications:
Petrochemical: Crude oil, gasoline, diesel pipeline transport in refining units.
Fertilizer: Ammonia (alkaline), urea solution pipeline boosting.
Chemical parks: Long-distance transfer of HCl or NaOH (head ≥80 m).
4. Selection Guide & Key Considerations
4.1 Pump Type Comparison
| Pump Type | Key Advantage | Material Options | Medium Compatibility | Installation | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extended Submersible Sewage Pump | Deep sump, anti-clog, long shaft | Cast iron / 304/316L SS | Large solids / fibrous wastewater | Submerged 1–10 m | Chemical wastewater, landfill leachate |
| Long-Shaft Vertical Submersible Pump | Ultra-long shaft, high head, large flow | Carbon steel / 304 SS | Fine solids in deep sump | Submerged 1–20 m | Crude oil tanks, deep pump stations |
| Stainless Steel Vertical Submersible Pump | Medium corrosion, submerged | 304/316L SS | Weak acid/alkaline, salt-containing liquids | Submerged 1–8 m | Pharmaceutical liquids, electroplating baths |
| Submersible Chemical Pump | High corrosion, zero leakage | Fluoroplastics / Hastelloy | Strong acid/alkaline, toxic, flammable | Submerged 1–5 m | Hazardous waste, fine chemicals |
| PVDF External Sump Pump | Strong corrosion, external installation | PVDF | Strong acids, organic solvents | External / pipeline | Semiconductor cleaning, lab experiments |
| General Vertical Chemical Pump | Pipeline transport, high head | 304/316L SS, fluoroplastic lining | Weak / strong corrosive media | Pipeline | Refinery, fertilizer, chemical park supply |
4.2 Selection Essentials
Medium First: Match corrosion resistance and solids content.
Solids → Extended Submersible Sewage Pump (open impeller).
Strong acids → Submersible Chemical Pump (fluoroplastics) or PVDF External Pump.
Weak corrosion → Stainless Steel Submersible Pump.
Installation Requirements: Know immersion depth and tank type.
Deep sump (>5 m) → Extended or Long-Shaft Submersible Pump.
Shallow sump (≤2 m) → PVDF External Pump.
Pipeline transfer → General Vertical Chemical Pump.
Safety Considerations: Zero leakage & explosion-proof features.
Toxic/flammable media → Submersible Chemical Pump (magnetic drive) or General Vertical Chemical Pump (double seal + nitrogen).
Explosive environments → Motor with Ex d IIB T4 certification.
These vertical pumps cover a wide range of chemical, environmental, and pharmaceutical applications, including submerged, external, high-corrosion, and debris-laden scenarios. Selecting the right pump requires careful consideration of media characteristics, installation depth, and safety requirements to avoid material mismatch, structural incompatibility, or operational hazards.