1. How Magnetic Drive Pumps Work
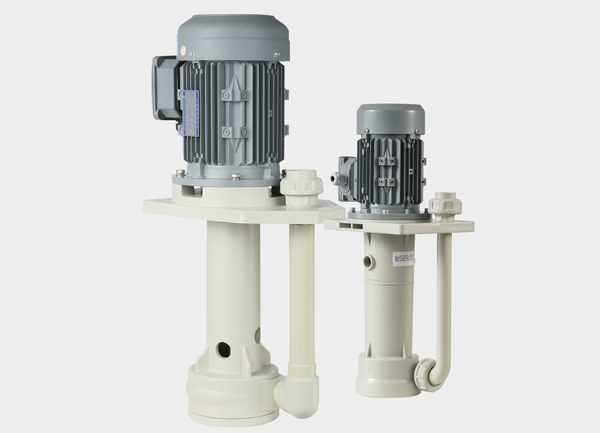
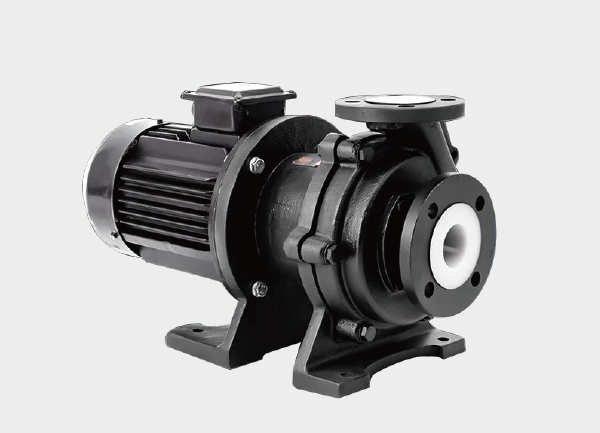
A magnetic drive pump, also known as a magnetically coupled pump, is a seal-less centrifugal pump that transfers torque from the motor to the impeller through magnetic coupling. Its main components include:
Outer magnetic rotor – directly connected to the motor and rotates with it.
Inner magnetic rotor – attached to the impeller and driven synchronously by the outer rotor through magnetic force.
Isolation sleeve – separates the inner and outer rotors, ensuring complete sealing of the pumped medium.
When the motor starts, the outer magnetic rotor rotates, creating a magnetic field that passes through the isolation sleeve to drive the inner rotor. The impeller then rotates, enabling the pump to suction and discharge liquid. Since there is no direct mechanical seal, leakage problems caused by seal wear are eliminated.

2. Key Advantages of Magnetic Drive Pumps
Zero Leakage Design
With a static sealing structure instead of a traditional dynamic shaft seal, magnetic drive pumps completely eliminate issues such as leakage, dripping, or vapor emission. This makes them ideal for handling toxic, hazardous, flammable, or explosive fluids.High Safety
The fully sealed pump chamber prevents harmful liquid from escaping, protecting workers’ safety and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.Low Maintenance Costs
Since there is no shaft seal to wear or replace, magnetic drive pumps have fewer failure points, longer service life, and lower maintenance costs compared to conventional pumps.Wide Chemical Compatibility
Suitable for strong acids, alkalis, organic solvents, and other corrosive liquids, as well as high-purity fluids that require contamination-free pumping. They are widely used in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, plating, and environmental protection industries.Smooth Operation & Low Noise
With no direct contact between rotating parts, magnetic drive pumps operate with minimal vibration, reduced noise, and low mechanical wear.Energy Efficiency
Thanks to high transmission efficiency and excellent sealing, energy losses are minimized, making magnetic drive pumps more efficient and cost-effective.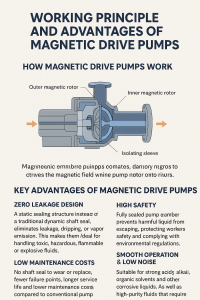
3. Applications of Magnetic Drive Pumps
Chemical industry – safe handling of corrosive acids, alkalis, and volatile solvents.
Pharmaceutical industry – transfer of sterile or high-purity liquids without contamination.
Environmental protection – wastewater treatment, circulation of hazardous liquids.
Electronics industry – pumping high-purity chemicals for chip and semiconductor manufacturing.
4. Conclusion
Magnetic drive pumps combine seal-less technology, safety, and durability, making them one of the most reliable solutions for fluid transfer in industries with strict environmental and safety requirements. With the global demand for safer and cleaner operations, the adoption of magnetic drive pumps will continue to grow.






