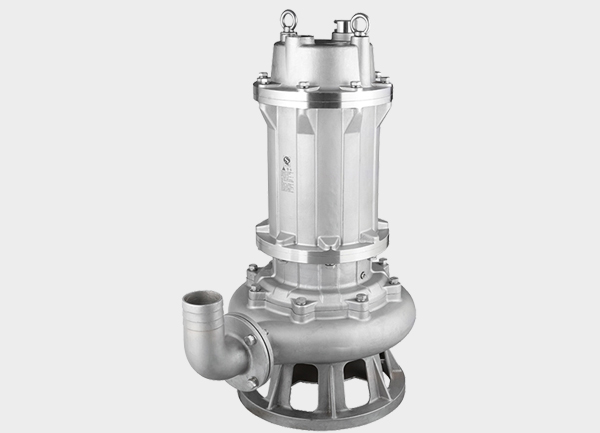
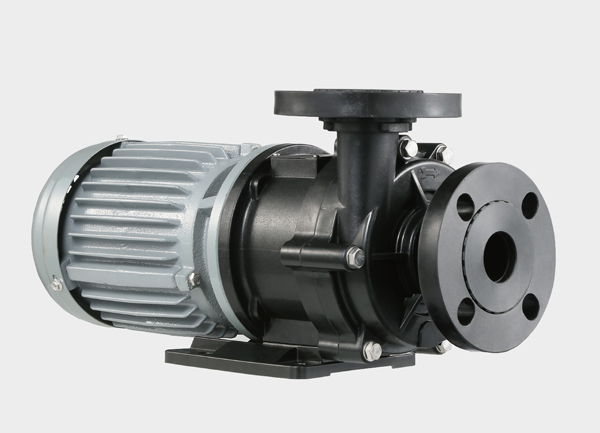
In modern industry, industrial magnetic pumps have become essential fluid transfer equipment thanks to their leak-free design, safety, and corrosion resistance. Unlike traditional mechanically sealed pumps, a magnetic drive pump uses magnetic coupling transmission, eliminating shaft seals and preventing leakage. This makes them highly reliable in chemical, pharmaceutical, environmental, food, and metallurgical applications.
This guide provides an in-depth look at the working principle, classifications, key applications, selection criteria, and maintenance practices of magnetic pumps. It also compares stainless steel magnetic pumps and fluoroplastic magnetic pumps, helping users make better decisions for their industrial needs.

1. Working Principle of Magnetic Drive Pumps
A magnetic drive pump consists of a driving magnet, containment shell, driven magnet, and impeller. The motor rotates the external magnet, which transfers torque to the internal magnet and impeller through magnetic force, thereby pumping liquid.
Key features include:
No mechanical seal → completely eliminates leakage.
Containment shell protection → ensures full isolation between liquid and drive components.
Handles complex media → suitable for strong acids, alkalis, high-temperature liquids, and high-purity media.
Relevant keywords: magnetic drive centrifugal pump, magnetic gear pump, magnetic circulation pump, magnetic turbine pump, leak-free magnetic drive pump.
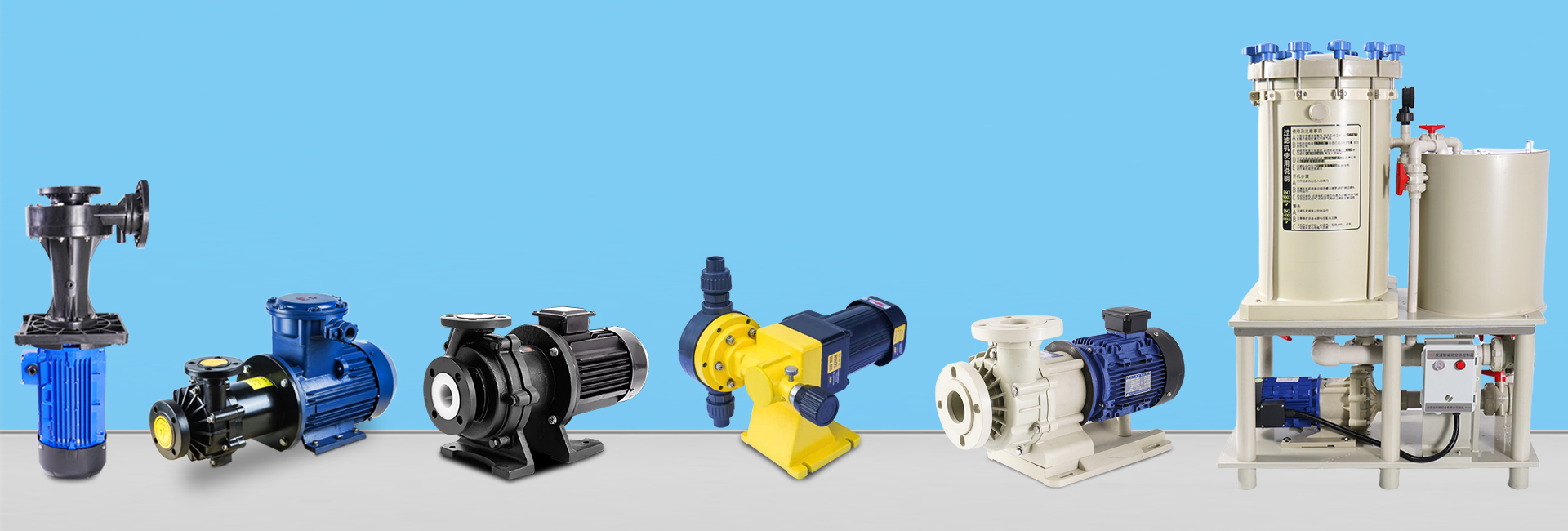
2. Main Classifications of Magnetic Pumps
(1) By Structure
Magnetic drive centrifugal pump: Widely used for low-viscosity liquids such as water and acid solutions.
Magnetic drive gear pump: Designed for high-viscosity liquids such as oils, lubricants, and resins.
Magnetic circulation pump / magnetic drive circulation pump: Used in cooling and heat exchange systems.
Magnetic turbine pump: Suitable for flammable or explosive media.
(2) By Material
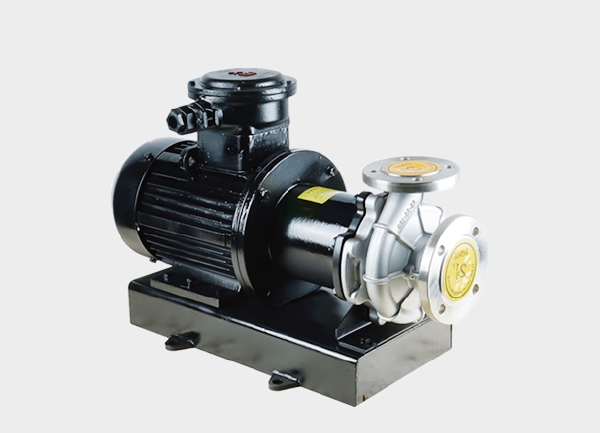
Stainless steel magnetic pump: Strong, corrosion-resistant, ideal for petrochemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries.
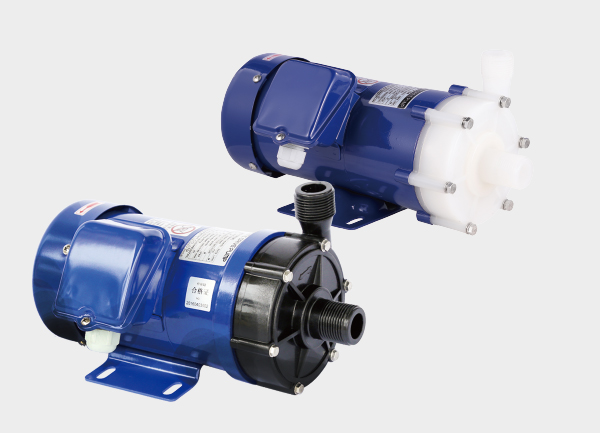
Fluoroplastic magnetic pump (TMF magnetic pump): Highly resistant to strong acids and alkalis, used in chemical and metallurgical applications.
Plastic magnetic drive pump: Lightweight, economical, and suitable for mild corrosive liquids.
(3) By Performance
High-temperature magnetic drive pump: Handles fluids up to 350℃.
High-pressure magnetic drive pump: Used in pressurized pipelines and reactor circulation.
Self-priming magnetic pump / self-priming magnetic drive pump: Eliminates the need for manual priming, convenient for frequent starts.
Small magnetic drive pump: Compact design for laboratories and small equipment.
3. Typical Applications of Industrial Magnetic Pumps
Chemical Industry
Transfer of highly corrosive media such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and hydrofluoric acid.
Recommended: fluoroplastic magnetic pumps / TMF fluoroplastic magnetic pumps.
Environmental Protection & Water Treatment
Used for wastewater treatment and acid-alkali neutralization systems.
Common choice: magnetic circulation pumps, magnetic drive circulation pumps.
Pharmaceutical & Food Industry
Applications with strict hygiene and safety requirements.
Preferred: stainless steel magnetic pumps, ensuring purity and no contamination.
Metallurgy & Electroplating
Transfer of plating solutions and electrolytes, requiring strong corrosion resistance.
Recommended: fluoroplastic magnetic pumps / plastic magnetic drive pumps.
High-Temperature & High-Pressure Systems
Reactor circulation and boiler feed applications.
Suitable models: high-temperature magnetic drive pumps, high-pressure magnetic drive pumps.
4. Key Factors in Selecting a Magnetic Pump
When choosing an industrial magnetic pump, consider the following factors:
Medium properties: temperature, pressure, corrosiveness, viscosity.
Flow rate and head: determine the required model and motor power.
Material selection: acids and alkalis → fluoroplastic; neutral media → stainless steel.
Self-priming capability: required for frequent start/stop operations → self-priming magnetic pumps.
Leak prevention requirements: hazardous chemical transfer → leak-free magnetic drive pumps.
Related keywords: magnetic pump price, magnetic pump suppliers, magnetic pump manufacturers, stainless steel magnetic pumps in China, high-quality TMF fluoroplastic magnetic pumps.
5. Maintenance and Operating Recommendations
Avoid dry running: running without liquid causes severe damage to the containment shell.
Regularly check the cooling circuit: ensure adequate lubrication and cooling of bearings.
Select pumps carefully: oversizing or undersizing reduces efficiency and lifespan.
Replace wear parts periodically: such as bearings and containment shells.
6. Conclusion
From stainless steel magnetic pumps to fluoroplastic magnetic pumps, industrial magnetic pumps have become indispensable in modern production processes. Whether you need a leak-free magnetic drive centrifugal pump, a self-priming magnetic pump, or a high-temperature magnetic drive pump, these solutions ensure safety, reliability, and efficiency in fluid handling.
When purchasing, always evaluate working conditions, pump materials, performance requirements, and supplier reputation to guarantee long-term, stable operation.